redis源码阅读-事件
redis服务器是一个事件驱动程序。当触发一个事件时,redis会创建一个事件,放入到待处理的队列,依次进行处理。
redis事件分为文件时间和时间事件。
文件事件:文件事件是对套接字操作的抽象,当服务器与客户端进行通讯,会产生出各种文件事件,而服务器则通过监听并处理这些事件来完成一系列网络通讯操作。
时间事件:redis一些操作是需要定时进行执行的,而时间事件就是对这类操作的抽象。
事件的实现
以下是事件结构体定义。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
/* File event structure */
typedef struct aeFileEvent {
int mask; // one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE) 类型
aeFileProc *rfileProc; // 读事件处理器
aeFileProc *wfileProc; // 写事件处理器
void *clientData; // 多路复用库的私有数据
} aeFileEvent;
/* Time event structure */
typedef struct aeTimeEvent {
long long id; // 唯一标志
long when_sec; // 事件到达事件s
long when_ms; // 事件到达事件ms
aeTimeProc *timeProc; // 事件处理函数
aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc; // 事件释放函数
void *clientData; // 多路复用库的私有数据
struct aeTimeEvent *next; // 指向下一个时间事件结构,形成链表
} aeTimeEvent;
/* A fired event */
// 触发的事件结构体
typedef struct aeFiredEvent {
int fd; // 文件事件描述符
int mask; // one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE) 类型
} aeFiredEvent;
// 事件循环结构体
typedef struct aeEventLoop {
int maxfd; // 当前注册的最大描述符
int setsize; // 需要监听的描述符个数
long long timeEventNextId; // 下一个时间事件ID
time_t lastTime; // 上一次时间循环时间
aeFileEvent *events; // 注册要使用的文件时间
aeFiredEvent *fired; // 已准备好,待处理事件
aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead; // 时间事件
int stop; // 事件处理器开关
void *apidata; // 处理多路服用库的私有数据
aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep; // 处理事件前要执行的函数
} aeEventLoop;
|
事件处理流程
redis使用i/o多路复用程序同时监听多个套接字,并根据套接字目前执行的任务来为套接字关联不同的事件处理器。文件处理流程如图。时间事件则定时执行。
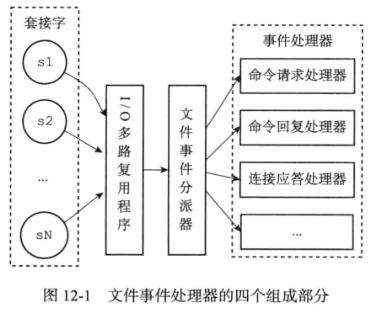
图片(来自《Redis设计与实现》
## 事件的API
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/* Prototypes */
aeEventLoop *aeCreateEventLoop(int setsize); // 初始化时间处理器状态
void aeDeleteEventLoop(aeEventLoop *eventLoop); // 删除事件处理器
void aeStop(aeEventLoop *eventLoop); // 停止事件处理器
int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask,
aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData); // 根据mask参数,监听fd文件的状态,fd可用,执行proc函数
void aeDeleteFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask);// 将fd从mask指定的监听队列中删除
int aeGetFileEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd); // 获取给定fd正在监听的事件类型
long long aeCreateTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long milliseconds,
aeTimeProc *proc, void *clientData,
aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc); // 创建时间事件
int aeDeleteTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id); // 删除给定ID的时间事件
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags); // 处理所有已经到达时间的事件,以及所有就绪的文件事件
int aeWait(int fd, int mask, long long milliseconds); // 指定时间等待fd变为可读、可写
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop);// 事件处理主循环
char *aeGetApiName(void); // 返回所使用的多路服用库的名字
void aeSetBeforeSleepProc(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep); // 设置事件前所需要执行的函数
int aeGetSetSize(aeEventLoop *eventLoop); // 返回当前事件槽大小
int aeResizeSetSize(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int setsize); // 调整事件槽大小
|
文件事件的创建
文件事件有三个方面需要创建:
- 连接应答处理器,用来处理对连接服务器监听套接字的客户端进行应答。
- 命令请求处理器,用来处理从套接字读取客户端发送的命令请求内容。
- 命令回复处理器,用来处理执行命令后得到的命令回复通过套接字返回给客户端。
连接应答处理器
acceptTcpHandler是连接应答处理器,当监听套接字产生AE_READABLE事件时,就会引发连接应答处理器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
void initServer() {
// ...
// 为 TCP 连接关联连接应答(accept)处理器
for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE,
acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR)
{
redisPanic(
"Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event.");
}
}
// 为本地套接字关联应答处理器
if (server.sofd > 0 && aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,server.sofd,AE_READABLE,
acceptUnixHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) redisPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.sofd file event.");
// ...
}
|
命令请求处理器
在连接应答处理器调用的函数acceptTcpHandler中,会在连接成功之后,创建命令请求处理器readQueryFromClient(),在客户端发送的命令请求时,调用命令请求处理器进行处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
// 创建一个 TCP 连接处理器
void acceptTcpHandler(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
int cport, cfd, max = MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL;
char cip[REDIS_IP_STR_LEN];
REDIS_NOTUSED(el);
REDIS_NOTUSED(mask);
REDIS_NOTUSED(privdata);
while(max--) {
// accept 客户端连接
cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport);
if (cfd == ANET_ERR) {
if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK)
redisLog(REDIS_WARNING,
"Accepting client connection: %s", server.neterr);
return;
}
redisLog(REDIS_VERBOSE,"Accepted %s:%d", cip, cport);
// 连接完成,创建一个客户端状态
acceptCommonHandler(cfd,0);
}
}
#define MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL 1000
static void acceptCommonHandler(int fd, int flags) {
// 创建客户端
redisClient *c;
if ((c = createClient(fd)) == NULL) {
redisLog(REDIS_WARNING,
"Error registering fd event for the new client: %s (fd=%d)",
strerror(errno),fd);
close(fd); /* May be already closed, just ignore errors */
return;
}
// 达到上限
if (listLength(server.clients) > server.maxclients) {
char *err = "-ERR max number of clients reached\r\n";
if (write(c->fd,err,strlen(err)) == -1) {
}
// 更新拒绝连接数
server.stat_rejected_conn++;
freeClient(c);
return;
}
server.stat_numconnections++;
c->flags |= flags;
}
redisClient *createClient(int fd) {
redisClient *c = zmalloc(sizeof(redisClient));
// -1时使用的是无网络连接的伪客户端
if (fd != -1) {
anetNonBlock(NULL,fd); // 非阻塞
anetEnableTcpNoDelay(NULL,fd); // 关闭nagle算法,那个合并小报文的算法
if (server.tcpkeepalive)
anetKeepAlive(NULL,fd,server.tcpkeepalive);
// 创建命令请求处理器
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE,
readQueryFromClient, c) == AE_ERR)
{
close(fd);
zfree(c);
return NULL;
}
}
// 客户端的初始化
// ...
}
|
命令回复处理器
当服务器有命令回复需要传送给客户端时,服务器将客户端套接字的AE_WRITABLE事件与命令回复处理器关联,当客户端准备好接收时,就会执行AE_WRITABLE事件,触发命令回复处理器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
int prepareClientToWrite(redisClient *c) {
if (c->flags & REDIS_LUA_CLIENT) return REDIS_OK;
if ((c->flags & REDIS_MASTER) &&
!(c->flags & REDIS_MASTER_FORCE_REPLY)) return REDIS_ERR;
if (c->fd <= 0) return REDIS_ERR; /* Fake client */
// 为客户端套接字安装写处理器到事件循环
if (c->bufpos == 0 && listLength(c->reply) == 0 &&
(c->replstate == REDIS_REPL_NONE ||
c->replstate == REDIS_REPL_ONLINE) &&
aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, c->fd, AE_WRITABLE,
sendReplyToClient, c) == AE_ERR) return REDIS_ERR;
return REDIS_OK;
}
|
时间事件的创建
redis在初始化时创建时间时间,用来周期执行serverCron()。
serverCron()主要功能:
- 更新服务器的各类统计信息
- 清理过期的键值对
- 关闭和清理连接失效的客户端
- 尝试AOF\RDB持久化
- 主服务器则定期同步
- 集群模式,对集群定期同步和连接测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
void initServer() {
// ...
// 为 serverCron() 创建时间事件
if(aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) {
redisPanic("Can't create the serverCron time event.");
exit(1);
}
// ...
}
|
事件循环
事件循环主函数为aeMain(),该函数在redis的main()函数中被调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// ...
// 运行事件处理器,一直到服务器关闭为止
aeSetBeforeSleepProc(server.el,beforeSleep); // 设置事件前调用函数
aeMain(server.el);
// 服务器关闭,停止事件循环
aeDeleteEventLoop(server.el);
return 0;
}
|
事件循环的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
|
// 事件处理器的主循环
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
// 如果有需要在事件处理前执行的函数,那么运行它
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
// 开始处理事件
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS);
}
}
// 事件处理函数
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
int processed = 0, numevents;
// 没有需要处理的事件则返回
if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0;
if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 ||
((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) {
int j;
aeTimeEvent *shortest = NULL;
struct timeval tv, *tvp;
// 获取最近的时间事件
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))
shortest = aeSearchNearestTimer(eventLoop);
if (shortest) {
long now_sec, now_ms;
/* Calculate the time missing for the nearest
* timer to fire. */
aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms);
tvp = &tv;
tvp->tv_sec = shortest->when_sec - now_sec;
if (shortest->when_ms < now_ms) {
tvp->tv_usec = ((shortest->when_ms+1000) - now_ms)*1000;
tvp->tv_sec --;
} else {
tvp->tv_usec = (shortest->when_ms - now_ms)*1000;
}
// 获取要执行事件事件,要等待的时间
if (tvp->tv_sec < 0) tvp->tv_sec = 0;
if (tvp->tv_usec < 0) tvp->tv_usec = 0;
} else {
// 没有时间事件
// 根据AE_DONT_WAIT参数来设置文件事件的阻塞、阻塞时间
if (flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) {
tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0;
tvp = &tv;
} else {
/* Otherwise we can block */
tvp = NULL; /* wait forever */
}
}
// 调用io复用函数获取准备好的事件,底层使用select或epoll或其他实现
// tvp阻塞时间
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
// 获取所有能够执行的文件事件,并执行
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd];
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
int rfired = 0;
/* note the fe->mask & mask & ... code: maybe an already processed
* event removed an element that fired and we still didn't
* processed, so we check if the event is still valid. */
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
// 读事件
rfired = 1;
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
// 写事件
if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc)
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
processed++;
}
}
/* Check time events */
// 执行时间事件,在阻塞等待一段时间之后,时间事件已经能够执行
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS)
processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop);
return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */
}
|
小结
事件其实不算复杂,整个redis没有太多的事件。但是要理解IO多路服用和redis事件的调用逻辑。理清楚之后就比较好办了。
 图片(来自《Redis设计与实现》
## 事件的API
图片(来自《Redis设计与实现》
## 事件的API